Both red tide and seasonal Sargassum are natural occurring phenomena and both are exacerbated by human activity which is mostly excessive nutrients in water. Now this seaweed is becoming more abundant and toxic, just one more negative aspect of our planet-destroying excesses heading all of us in the wrong direction.
Stringy, smelly algae dominates coastline from Cocoa Beach to Sebastian and beyond
 Jim Waymer Florida Today
Jim Waymer Florida Today
This summer, some say things look a bit — and smell a bit — worse than usual. That’s because the shoreline seems mostly awash in weeds, from Cocoa Beach to Sebastian Inlet and beyond.
There’s the usual Sargassum, which the Caribbean Sea delivers seasonally to the Gulf Stream and then Central Florida’s beaches.
But some “filamentous” algae has been dominating the surf zone this summer, to the bane of fishers, surfers and all others who prefer weed-free wading, scientists at Florida Atlantic University say.
Oceanographers expect Sargassum seaweed and other macroalgae to thicken on our beaches every year. It comes from the eastern Caribbean and spreads throughout Florida’s east coast and elsewhere.
Winds dictate when these stringy weeds lap up on our shore.
‘Sargassum storm’:Stinky seasonal seaweed sets record in Brevard, and more is coming this way
Seasonal seaweed strikes back: Tons of seaweed washes up on the Space Coast
For centuries, pelagic Sargassum, floating brown seaweed, have grown in low nutrient waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, supported by natural nutrient sources such as fish and invertebrates excretions and ocean upwelling. But as fertilizers, wastewater and other human source have increased the nitrogen and phosphorus into rivers, that seaweed as well — as the filamentous kind we’re seeing so much of now — has been growing out of control over the past decade.
Florida Atlantic University researchers have for years shown seasonal Sargassum here and elsewhere in the tropical Atlantic has grown worse in recent years because of increasing nitrogen and phosphorus from discharges from the Congo, Amazon and Mississippi rivers, atmospheric deposition from Saharan dust, and biomass burning of vegetation in central and South Africa,
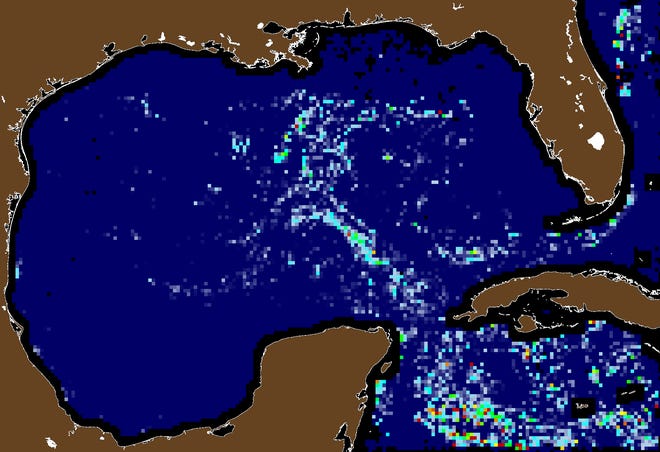
This summer’s Sargassum already has set a record. Combined, the total amount of the weed increased from 18.8 million tons in May 2022 to 24.2 million tons in June 2022, setting a new historical record, according to the University of South Florida scientists July 2 bulletin on the algae.
Considering the historical record-high mass of Sargassum in June, more of the seagrass may enter the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico in the following months, riding major ocean currents, USF bulletin warns. USF runs a Sargassum Watch System.
The University of South Florida expects the trend of increasing Sargassum seaweed in the ocean to slow this month but with the possibility of ramping back up after that.
A year ago, fed by sewage and fertilizers in Brazil and thereabouts, the same seaweed kept coming all summer long. FAU at the time released a study that suggested increased availability of nitrogen from natural and man-made sources, including sewage, fuels excess Sargassum growth.
According to the study, our waste can turn a critical nursery habitat into toxic algae dead zones, “with catastrophic impacts on coastal ecosystems, economies, and human health.”
The FAU researchers used unique historical baseline seaweed tissue from the 1980s to compare its chemical makeup to samples collected since 2010. They found dramatic changes in the chemistry and composition of Sargassum weed since the 1980s, “transforming this vibrant living organism into a toxic “dead zone,” FAU’s announcement said.
Their findings were published last year in Nature Communications.
Washed-up Sargassum:Washed-up Sargassum seaweed sometimes wreaks havoc and reeks; expect it for next several weeks
Pulled from waves:Several pulled from waves after boat capsizes near Melbourne Beach
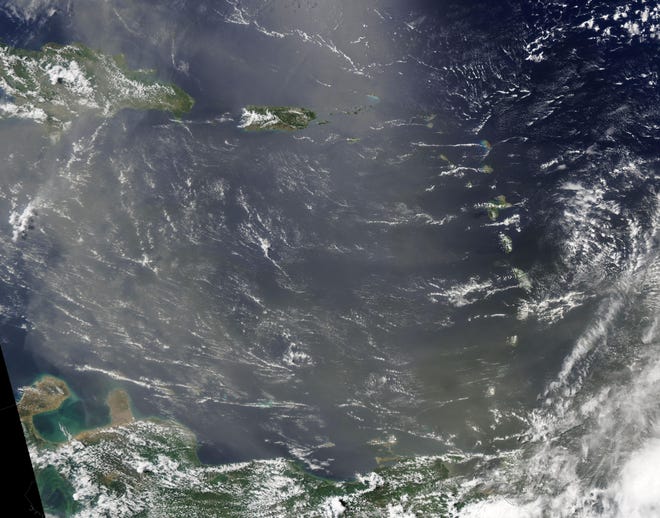
Last month, strong winds blew a thick layer of dust from the Sahara Desert westward over the Atlantic Ocean. By June 6, the leading edge of the massive river of dust reached South America, stretching more than 3,500 miles and covering more than 2.2 million square miles, according to the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on board NASA’s Aqua satellite, which acquired a true-color image.
Biologists say the vegetation washing up on the Space Coast and shorelines statewide this month usually is beneficial to the beach. It provides food for birds, crabs and other wildlife and habitat for hiding. So raking the stuff off the beach can be controversial, often pitting tourism against conservation interests.
But when the weed feeds off too much sewage, it can turn toxic for some wildlife, FAU and other research shows.
Sargassum is a constant presence in the Atlantic. It typically drifts in long lines near the Gulf Stream and provides vital food for young sea turtles. In excess, though, the stuff annoys tourists and those who’s livelihoods depend upon them, by fouling the beaches beauty and air.
Sargassum contains arsenic, which it uptakes from what’s naturally in ocean water. But arsenic levels have been increasing in the seaweed as humans have contributed more nitrogen to the environment, FAU researchers say. As humans have added more nitrogen from fertilizers, sewage, deforestation and other sources to coastal waters, seaweed and other aquatic plants seek more phosphates to balance their nutrients. In doing so, the plants uptake more arsenic because its in a molecular form that’s similar to phosphate.
The recent stringy mess on Brevard County beaches reminds many on the beach side of widespread Sargassum algae blooms that hit county beaches in 2014, 2015, 2018 and last year. Huge Sargassum blooms blanketed beaches along the east coast of Barbados and Puerto Rico in 2014, as well. But 2018 was among the worst in Florida, Lapointe said, adding that this year could rival that year’s bloom.
Jim Waymer is an environment reporter at FLORIDA TODAY. Contact Waymer at 321-261-5903 or jwaymer@floridatoday.com. Or find him on Twitter: @JWayEnviro or on Facebook: www.facebook.com/jim.waymer






